ARDN
The Agricultural Research Data Network (ARDN)
There is a major gap between the potential value of data collected in agricultural experiments and the value currently obtained through use of those data. Typically, data collected in experiments are used for the original research purpose only. Vastly greater value might be obtained if the data were combined across locations, time, and management conditions. The Agricultural Research Data Network provides tools and protocols to allow researchers to not only share their data, but to make their data interoperable and reusable. Additional tools allow end users of the data to combine and reformat ARDN data for quantitative analysis and modeling.
Why ARDN?
The goal of ARDN is to create a distributed network for harmonized crop systems research data and to make these data available through existing data portals such as USDA’s Ag Data Commons and CGIAR’s GARDIAN. For more information, see Why ARDN?
What is ARDN?
Data Network: ARDN is a network of datasets which can be harmonized and aggregated using a common vocabulary and format.
Data Interoperability Protocol: Datasets in ARDN are connected by a common protocol for annotating data which allows the data to be interpreted in an automated way. More information, see What is ARDN?
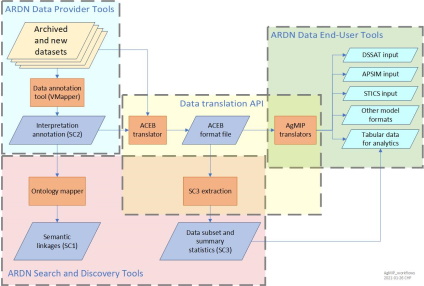
The diagram below shows the main workflows associated with ARDN.
For larger image, click here
Who are ARDN users?
ARDN data providers have data that they wish to make available to researchers in a format that can be interpreted in an automated way. ARDN tools assist these users to “ARDN-ize” their data thereby making these datasets reusable.
End users of ARDN data make use of the interoperability of these datasets and can download and transform the data into formats that can be used in modeling applications, data analytics, meta-analyses, and other quantitative uses.
There are several data portals that are implementing ARDN protocols. ARDN has been implemented on Ag Data Commons, the data and publication portal of the USDA National Agricultural Library. Compatible data interoperability standards are also being developed and implemented on the CGIAR GARDIAN platform and by the International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC). For more information, see Why ARDN?
What ARDN is NOT:
- ARDN does not (yet) include data from other agricultural domains such as livestock, pest and diseases, aquaculture, socioeconomics, and genetics. Similar methods could be developed for these domains.
- ARDN is mainly developed for quantitative data that are used in modeling and analytics. It is less useful for categorical data, such as color, or categorical scales of damage, or other information.
- ARDN is most useful for “legacy” data where the format and vocabulary of the dataset are not standardized.
We hope that in the future, datasets are collected from the field using standardized vocabularies and ontologies so that the ARDN data annotation method is no longer needed. But until then, we offer these interoperability hacks!
How does ARDN work?
Datasets in the ARDN network have been annotated to allow automated interpretation of the contents of the dataset. This is done primarily through the use of three Sidecar Files, which can be thought of as extended metadata.
Sidecar file 1 allows semantic linkage of the dataset to ontological terms.
The primary component of ARDN annotation is Sidecar file 2, which allows the original dataset, without modification, to be interpreted and converted to AgMIP ACEB format. Once datasets have been harmonized to AgMIP format, they may be combined and translated to various end-user formats.
Sidecar file 3 contains a subset of the data in a dataset in a tabular format and summary statistics for the dataset. This allows the data portal to conduct rapid, complex searches on the contents of the data without accessing or interpreting the data.
For more detailed information about ARDN protocols, workflows, and tools, see How does ARDN work? Additional information can be found by the following links:
- ARDN dataset annotation
- AgMIP data format
- ICASA vocabulary
ARDN Glossary and References
A list of ARDN terms, acronyms, and related references can be found here.